Let’s face it, weeds can be a gardener’s worst nightmare. But determining how to clear a garden full of weeds is a bit more complex than it seems. Although weeds are invasive, hard to eliminate, and can wreak havoc on your beautiful garden throughout the season, it’s worth getting them under control to maintain the health and vitality of your green space. And while pesky weeds are part of the natural order of garden life, as a responsible grower, you must stand firm to protect your turf.
Weeds compete with garden plants for resources, harbor pests, spawn disease, and can regenerate aggressively from resilient roots. To prevent weeds, hand weeding, applying herbicides, and cultural practices help manage weed proliferation. In contrast, some simple DIY control methods, including soil prep, plant selection, and mulching, help control weed growth.

As a humble gardener, it’s best to be prepared when battling weeds in your food oasis. And with these excellent tips, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, we’ve got you covered.
In this article, I will cover various weed removal and prevention methods so you can reclaim your garden and enjoy its natural beauty without the constant frustration of weed invasions. Let’s do this!
Humble Highlights
- Discover the four standard weed tool classifications to help you rid your garden of pesky weeds AND save money by learning which works best for you.
- Learn the differences between organic and chemical weed options so you can effectively kill weeds in the least amount of time.
- Save time by uncovering the 4 primary weed control techniques so you can use these critical resources to your advantage throughout each growing season PLUS so much more!
Why Weeds Are A Problem
Besides being unsightly, weeds can pose several significant challenges to your garden. First, weeds compete with your desired plants for vital resources such as water, sunlight, and soil nutrients. Moreover, weeds offer shelter to pests and diseases, which can quickly spread throughout your garden. Thus, taking steps to eliminate these unwanted invaders from your garden is crucial.

But before eliminating these nagging weeds, getting to know them first is recommended because, surprisingly, some weeds can benefit your vegetable plants within your growing area. So, understanding and identifying weeds might help you discover the perfect solution to eliminate the harmful ones from your garden. Victory indeed takes patience. 1
Weapons Of Mass Weed Destruction: The Weed Terminator Tools
Several essential weed tools remain popular with today’s gardeners in helping to effectively pluck weeds from their green space. The most common include:
- Hand Tools
- Power Tools
- Farm Implements
- Protective Gear

Let’s look at these instruments to help you understand which may work best for you.
Hand Tools
Hand tools are simple, light tools that can be used with bare hands or gloves within small areas. Examples include:
- The hand fork for weeding and mixing additives into the soil.
- The hand cultivation tool for loosening the soil.
- The hand trowel is for digging, loosening soil, and transplanting seedlings.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Hand Tool Kits
Power Tools
Power tools are an excellent option for gardeners with large areas to maintain or deal with stubborn and established weeds. Weed whackers, or string trimmers, can quickly and easily remove weeds in areas a lawn mower may not reach, such as along fence lines or around trees, retaining walls, and other obstacles. Chainsaws can cut down more enormous, woody weeds like saplings or invasive shrubs. 2
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Weed Whackers
Farm Implements
Farm implements are accessories pulled by working animals or mounted machinery used to prepare the rural or commercial farm. Examples include:
- The plow is used for dealing with large land areas, making furrows, and row cultivation.
- The harrow is used for peeling and pulverizing the soil.
- The rotavator is mounted to a tractor and pulverizes large swaths of ground in preparation for planting.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Soil Tillers
Protective Gear
Protective gear is an essential aspect of weed management to ensure the safety of individuals performing these tedious but necessary tasks. Gloves should be used to protect hands from injury, blisters, and exposure to chemicals found in some herbicides. Long sleeves and pants can protect against scrapes, cuts, and contact with poison ivy or other irritants. Eye protection such as goggles or glasses can prevent eye damage from flying debris, dust, or chemical sprays.

Check Lowest Prices On The Best Safety Glasses
Weed Prevention Strategies: Organic vs. Chemical
Because weeds can be a continual burden in the garden, the two primary ways to help keep them under control include an organic DIY approach or non-organic chemical herbicides. Not only will these methods help improve the health and appearance of your vegetable plants, but they can also lead to better crop yields and lower costs.

Check out some of our top tips below for preventing and controlling weeds in your garden.
Organic DIY Approaches
Soil Preparation
Tilling your soil can help break up clumps of dirt and expose weed roots to sunlight, effectively drying them out and preventing them from growing further. This method helps prevent your seeds from continually seeding and proliferating at will in your garden. You can also use organic matter, like compost, to improve soil structure and fertility, giving your plants a better chance of competing with weeds.
Plant Selection And Spacing
Interestingly, choosing the right vegetable plants and spacing them correctly in your garden can help prevent weed growth. For example, fast-growing plants with leafy, dense canopies can shade out weeds and prevent them from getting enough sunlight to grow. Correctly placing plants can also help reduce competition for water and nutrients. Lettuce, tomatoes, beans, and cucumbers are just a few varieties that offer dense shady coverage.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Cucumber Seeds
Following the spacing instructions on the tag or seed bag is essential when planting starts or sowing seeds, respectively. And while you don’t have to be perfect, spacing your plants takes some practice, especially if you’re trying to combat weed growth throughout your garden.
While planting density can help prevent weeds by reducing the amount of bare and exposed soil in your garden where weed seeds germinate, growing too densely leads to overcrowding, disease, and resource competition. Instead, planting your garden beds with various plants can create a dense canopy that shades the soil and prevents weed growth without creating unnecessary foilage rivalries. 3
Applying A Thick Layer Of Mulch
Another excellent way to prevent weeds is to apply a thick layer of mulch over your garden beds. Mulch not only helps to suppress weeds but also helps conserve moisture in the soil, regulate soil temperature, and improve soil structure as it decomposes. Be sure to apply a thick layer of mulch, at least 2-3 inches deep, to maximize its weed-suppressing benefits.

Mulching your garden beds can also help to suppress weed growth by blocking sunlight. Organic mulches like straw, pine straw, leaves, or wood chips can also add nutrients to your soil as they decompose, benefiting your plants.
The two best times to layer a few inches of rich, organic compost atop your soil are a few weeks before planting in the spring and again in late fall, after the last harvest. So, investing in a compost tumbler or carving out a dedicated space in your backyard for an open-air compost pile is also a wise decision.
Other DIY Approaches
If stubborn weeds are still giving you fits, and you’d like your garden to remain organic, here are some other easy and effective DIY approaches any humble gardener can take.
- Scalding weeds with boiling water. Be careful you don’t burn yourself.
- Sprinkling salt along the edges of your lawn or garden pathways.
- Making homemade herbicide with white vinegar, salt, and dish soap.
- Suffocating weeds with old newspapers.
- Wetting the soil and pulling weeds out from the base when the soil is still moist.
The video below explains why staying on top of weed issues throughout the growing season is prudent so they won’t interfere with your essential vegetable plants that produce food. But humble gardeners go beyond just managing weed issues. Instead, they actively identify each of these undesirable plants so they can form better treatment options for the challenges these weeds impose.
Chemical: Pre-Emergent Herbicides
If you’re looking for a more powerful weed-killing option, pre-emergent herbicides can effectively prevent weed growth before it starts. However, these herbicides inhibit seed germination, so they must be applied before the weeds grow. As with any synthetic chemical, following the instructions carefully and avoiding using these herbicides near desirable plants is essential. Remember, you want to kill the weeds, not your food garden. 4
When you use synthetics, your space won’t be considered organic. Additionally, depending on the strength of the chemicals you may choose to apply, some may leave a lengthy residual on nearby plants and shrubs while leaching into the ground through runoff and potentially absorbed by other adjacent foliage. So, do use caution and protective gear, as mentioned above.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Herbicides
Overall, preventing weeds from growing in the first place saves you time and effort in the long run. Using a combination of prevention strategies like soil preparation, plant selection and spacing, mulching techniques, and pre-emergent herbicides (if necessary) can help keep your garden healthy and decrease the number of weeds wanting to call your garden home.
Weed Control Techniques: Manual, Chemical, Cultural, Biological
If you already have existing weeds in your garden, there are several methods you can use to prevent them from taking over and damaging your plants further, including:
- Hands-On: Manual Techniques For Controlling Weeds
- Chemical Control: Using Herbicides
- Cultural Weed Control: Garden Weeds Of Invasive Weeds
- Mother Nature’s Army: Biological Methods For Weed Control

Let’s examine each manual technique and biological control method to provide you with some excellent options you can consider for effective weed control.
Hands-On: Manual Techniques For Controlling Weeds
Hand-Pulling Smaller Weeds
One of the most basic, age-old, and effective ways to remove weeds is by hand-pulling them. This method involves grabbing the weed close to the soil surface (or just below) and pulling it out, removing the entire root system. Hand-pulling works best for minor weed infestations and can be done without special tools, making this an inexpensive and practical choice. 5
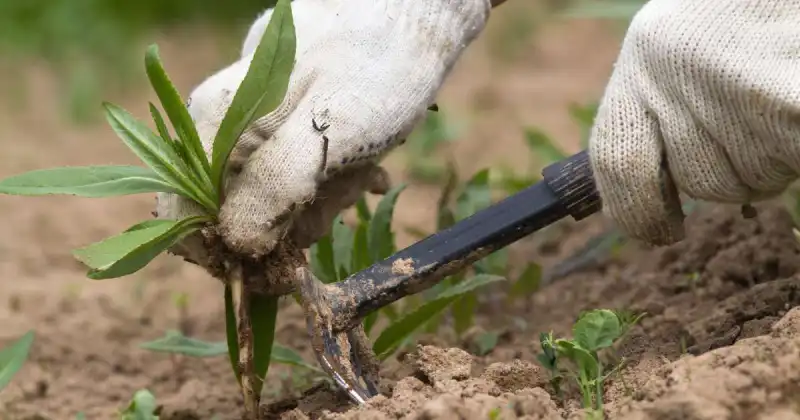

Hoeing Weeds In Larger Areas
Hoeing is another manual weed control technique that uses a hoe to cut off the weed head and disrupt the root structure below the soil surface. This method can effectively remove weeds in larger areas or areas where hand-pulling is not feasible. Hoeing works best on annual weeds and should be done when the soil is dry to prevent the weed from re-rooting.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Garden Hoes
Digging With A Shovel
Digging involves using a shovel or similar tool to dig out the weed and root system. This method can be effective for larger or more established weeds that are difficult to remove by hand or hoeing. However, shovel digging should be done carefully to avoid damaging nearby plants or disturbing the soil too much.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Garden Shovels
Uprooting For Sturdy Weeds
Uprooting is a technique that involves using a unique tool, like a weed wrench or weed puller, to remove the weed and its root system. This method can be effective for larger, more established weeds with taproots that are difficult to remove by other methods. However, as previously discussed, uprooting should be done carefully to avoid damaging nearby plants or disturbing the soil too much.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Weed Wrenches
To summarize, manual weed control techniques can remove weeds from your garden without synthetic chemicals. Using methods like hand-pulling, hoeing, digging, or uprooting, you can keep your garden healthy and lessen the chances weeds take over your growing area.
Chemical Control: Using Herbicides
While harsh, herbicides can significantly decrease the number of weeds in an area and quickly change the weed species’ dynamic. Here are a few herbicide options you may apply in your garden. Always read the package’s label for usage directions and wear proper safety gear.

Post-Emergent Herbicides
Post-emergent herbicides are a type of chemical herbicide that is applied to weeds after they have emerged. These herbicides kill the leaves and stem of the weed, which can also cause the roots to die off. Post-emergent herbicides can effectively control weeds, but they must be applied carefully to avoid damaging nearby plants.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Post-Emergent Herbicides
Selective Herbicides
Selective herbicides are designed to target specific types of plants, like broadleaf weeds or grassy weeds. This class of herbicides works by targeting enzymes unique to the targeted plants, making them less harmful to other plants. Selective herbicides can effectively control weeds while leaving your desirable plants unharmed.

Non-Selective Herbicides
Non-selective herbicides are designed to kill all types of plants, including desirable ones, leaving nothing behind. In addition, these herbicides kill the leaves and stems of the plant, which can cause the roots to die off as well. Therefore, non-selective herbicides should be used carefully and sparingly, as they can cause harm to nearby plants and animals. They may also leave a residual, so it’s best to consider how best to apply if this is your chosen route.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Non-Selective Herbicides
Organic Herbicides
Organic herbicides are made from natural ingredients like vinegar, salt, or essential oils. These herbicides can effectively control weeds without harsh chemicals, but they may need to be applied more frequently than chemical herbicides.
However, if your weed infestation is intensive and has overtaken your space, organic herbicides may not perform well, and you may need to opt for more potent chemical herbicides. And, like some chemical synthetics, use organic herbicides carefully to avoid damaging nearby plants.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Organic Herbicides
Cultural Weed Control: Garden Weeds Of Invasive Weeds
Savvy gardeners understand that cultural weed control methods also effectively kill unwanted weeds in their space. Although these options may take a bit of pre-planning, they are well worth it because they save the humble gardener loads of time in the long run while helping clear their space of many unwanted weeds.
Let’s look at some of these cultural weed control alternatives below.
Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is an agricultural technique that involves planting different crops in the same field yearly to help reduce disease and pest damage while reducing weed growth. By rotating your crops, you can effectively disrupt the life cycle of weeds and reduce the buildup of weed seeds in the soil.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Crop Rotation Books
Check Lowest Prices On Garden Log Books And Planners
Solarization
Solarization is a method of controlling weeds that involves covering a garden bed with clear plastic for about 7 to 8 weeks to heat the soil and kill weed seeds and pathogens. This method is simple yet effective for controlling weeds in the warmer summer months when the sun is at its strongest. By trapping heat under the plastic, the temperature of the soil can reach up to 140°F, which is hot enough to kill many weed seeds and pathogens. 6
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Tarps
Smother Cropping
Smother cropping involves planting cover crops that grow quickly and densely, shading out and suppressing weed growth. The cover crop can also help to improve soil health by incorporating organic matter and increasing soil moisture retention.

Cover cropping is especially effective for controlling weeds in areas with low soil fertility caused by unrestricted grazing or lack of energy sources. Additionally, using cover crops over the colder winter months helps crowd out weed seeds come spring, while the organic matter encourages beneficial microorganisms and worms to stay within your garden soil.
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Cover Crop Seed Mixes
Mowing And Cutting
Mowing and cutting is a simple and effective technique to help prevent weed seed production and reduce weed growth. You can help prevent weeds from spreading and taking over your food garden by cutting down weeds regularly. However, cutting weeds before they can flower and produce seeds is crucial, as cutting them after this stage will only spread the seeds and worsen the problem.
Mother Nature’s Army: Biological Methods For Weed Control
Suppressing weeds effectively in your vegetable garden sometimes is as easy as allowing Mother Nature to work on your behalf. Because specific insects and plants can help control your weed population, it makes wise sense for the humble gardener to maximize these wins whenever they can. Below are several key advantages of allowing nature to do your heavy lifting. 7
Insects Or Pathogens
Insects and pests can be a natural and effective way to control weeds in a backyard garden or a sizeable agricultural field. For example, some insects, such as the flea beetle or the gall fly, feed on weed seeds, which help reduce weed populations.
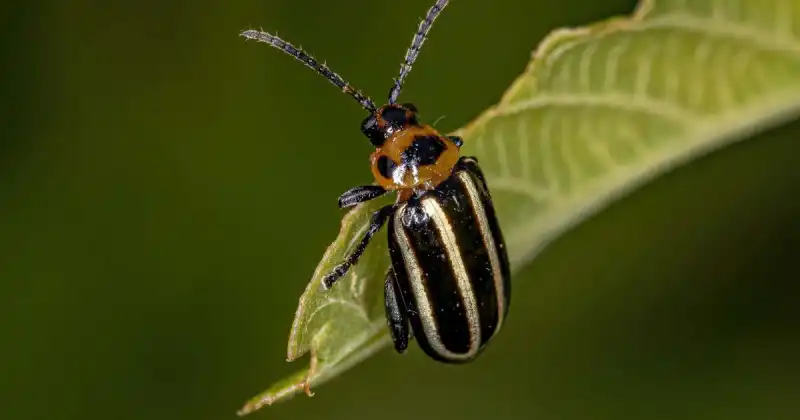

Additionally, some pests like the wireworm or cutworms feed on the roots of weeds, effectively killing them. However, caution is essential when introducing insects or pests to a garden, as they can also harm food-producing plants.
Allelopathic Plants
Some plants are known for suppressing weed growth by releasing certain compounds and chemicals into the soil that can curb and impede the development of other plants. These allelopathic plants can effectively control weeds in a garden or field. Examples of allelopathic plants include rye and sorghum. These plants can be grown as cover crops to help control weeds and used to create allelopathic mulches that any grower can spread over garden beds for effective results.
However, it’s best to use allelopathic plants carefully, as they can also inhibit the growth of desirable plants if not used properly or left to grow by their own will. Therefore, it’s important to research the specific plants used and follow recommended planting and cultivation practices.
Livestock Grazing
Livestock grazing is a natural and effective way to control weeds. Goats and sheep, along with free-range chickens, are known for their appetite for weeds, and they can help to keep weeds under control by eating the tops of the plants and their roots.
However, carefully managing livestock grazing is vital to prevent overgrazing and soil erosion. Overgrazing can lead to soil compaction and the loss of beneficial plant species, which may lead to the opposite results you desire; an increase in weed growth. Therefore, grazing should be well-monitored and controlled to avoid overgrazing. It’s also essential to keep your livestock on the move, periodically providing each pasture or field a break or resting period to allow the plants to recover.
The video below details how one gardener efficiently manages his garden by cutting weeds with a specialized hoe that cuts weeds below the surface. Although root systems are left intact, this method creates a “cleaner” grower area and saves time.
Planning And Timing Your Weed Control Efforts
There are three primary elements when it comes to planning and timing your weeding efforts, including:
- Assessing your weed infestation
- Prioritizing dense areas
- Coordinating accordingly with your region’s seasons, climate, temperature, and weather

Assessing Weed Infestation
Assessing the severity of a weed infestation is essential for developing an effective weed control program. This process involves identifying the types of weeds and measuring the infestation’s size and growth rate.
Further, this assessment helps determine the best methods to control these problematic weeds, like manual methods for small infestations and chemical or mechanical applications for larger, more extensive ones. Finally, the assessment can uncover underlying soil or environmental issues causing weed growth, such as poor soil health or nutrient imbalances, which you can remedy. 8
Prioritizing Areas For Weed Control
Prioritizing areas for weed control is a fundamental step in managing weed growth in your backyard garden. By identifying areas where weeds are most prevalent or pose the greatest threat to desirable plants, you can focus your primary efforts on the areas that need the most attention.

Starting weed control efforts within areas with the most prevalent weed growth can help prevent the weeds from spreading to other garden areas. For example, if you have a large patch of crabgrass in one corner of your garden, it’s essential to address that area before these aggressive weeds can spread to other, more prominent sites.
For example, suppose you have a vegetable garden with tomato plants constricted by a dense patch of weeds. In that case, it’s crucial to prioritize weed control in this area to ensure the tomatoes have the space, nutrients, and sunlight they need to grow and produce a good crop before moving on to a less critical area.
Coordinating With Seasons And Weather
Coordinating with your region’s seasons, temperatures, climate, and weather is essential to weed management. For instance, some herbicides are more effective when applied during specific weather conditions, such as when the temperature is above a certain threshold or when no rain is expected for a certain period. Similarly, hand weeding and cultivation may be more effective during certain seasons when the weeds are actively growing and easier to remove.
Although underutilized by many growers today, by planning weed management activities in sync with the seasons and weather, you can maximize the effectiveness of your efforts and reduce the likelihood of weed regrowth in the most critical areas of your garden.
Identifying Common Weeds
Before snatching onerous weeds from your growing area, a good gardener first identifies garden weeds to neutralize them effectively. Some of the most common garden weeds include:
- Grassy Weeds
- Broadleaf Weeds
- Invasive Species

Let’s take a better look at each of these familiar weed varieties.
Grassy Weeds
Grassy weeds are another common weed we are all accustomed to seeing. These weeds are plants with long, narrow leaves and are classified as monocots, which means they have a single cotyledon or seed leaf.
Grassy weeds are easily distinguished from broadleaf weeds, which have broader leaves, hence the name. Some common examples of grassy weeds include crabgrass, goosegrass, and annual bluegrass. These weeds can quickly take over a lawn, field, or backyard garden if left uncontrolled. 9
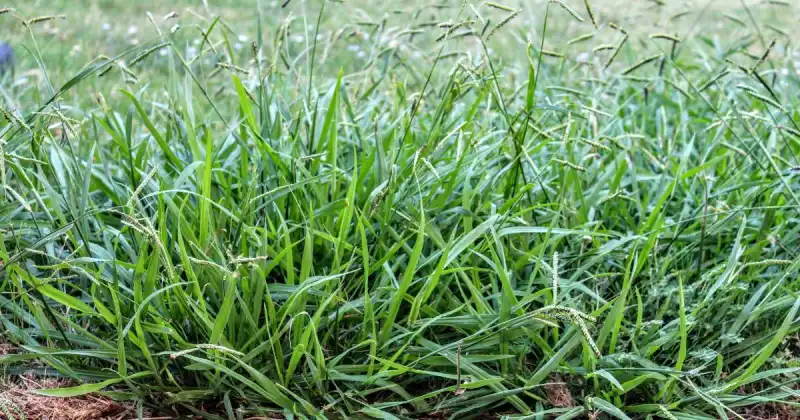

Fortunately, you can manage these weeds using hand weeding, herbicides, and cultural practices. Hand weeding is helpful for small infestations of grassy weeds or where herbicides cannot be applied. Herbicides also make a good option, but fewer selective herbicides exist for grassy weeds. As always, careful application of any chemical herbicide is necessary to avoid harming other plants. Proper mowing and watering practices can also help prevent grassy weeds from spreading.
Broadleaf Weeds
Broadleaf weeds are plants with broad, flat leaves classified as dicots (two cotyledons or seed leaves). These weeds can be a nuisance in gardens and lawns because they spread quickly and compete with other plants for soil nutrients, sunlight, and water. Some examples of this weed include dandelion, clover, chickweed, and plantain. You can use various methods to control broadleaf weeds, including hand weeding, chemical herbicides, and cultural practices like proper mowing and fertilization.
Invasive Species
Invasive weeds are non-native plants to your local area that may cause harm to the environment, economy, or even human health. Some common examples of invasive species you might come across include Japanese knotweed, purple loosestrife, and garlic mustard, to name a few.
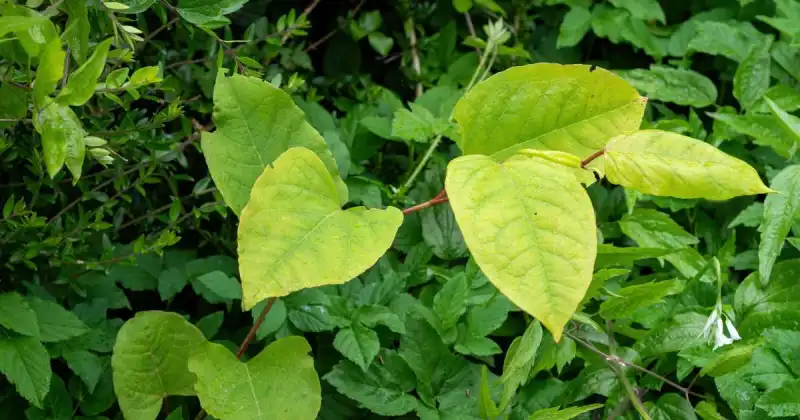

Dealing with invasive species can be tricky, sometimes requiring specialized methods like biological control or mechanical removal. But the best strategy is often prevention through early detection and rapid response. By catching invasive species early on, you can manage them more effectively, protect your garden, and save yourself from countless headaches.
Types Of Weed Growth Patterns: Annual, Biennial, And Perennial
Generally, weeds can be classified in various ways. One of the most common methods in classifying weeds is the plant’s life cycle. This process involves looking at factors like the length of life, season of growth, and time and method of reproduction. Under this life cycle method, there are three classifications: annual, biennial, and perennial.
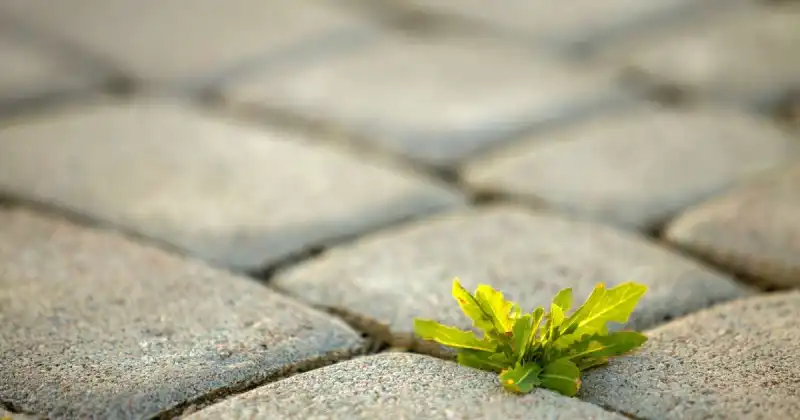

Annual Weeds
An annual plant, for instance, completes its life cycle from seed to seed in one year or less. There are two groups of annuals, winter and summer, which are determined by the plant’s germination, maturation, and termination time.
Winter annuals typically germinate during the fall or winter, grow in the spring, and die by early summer after setting seeds. On the other hand, summer annuals germinate in the spring, grow through the summer, set seeds by fall, and expire before winter. 10
Annual plants comprise the largest group of weeds, commonly sprouting between sidewalk cracks and flower gardens everywhere.

Biennial Weeds
Biennials are plants that live longer than one year but less than two. These biennial weeds develop from a seedling into a rosette during their first growth phase. Interestingly, this growth habit can sometimes make biennials look like winter annuals. However, after the cold weather passes, these weeds resume growing, produce flowers and seeds, and then die off.
Perennial Weeds
Perennial weeds have a longer lifespan and reproduce multiple times from the same root system. For example, simple herbaceous perennials regenerate from seeds and from injured or cut roots. Creeping herbaceous perennials produce new structures from asexual reproductive organs and sexually from seeds. Woody plants have secondary growth, producing wood and bark, and include trees, shrubs, and many vines. Lastly, aquatic weeds are mostly creeping herbaceous perennials, and some perennial weeds are woody plants.
Therefore, knowing the different types of perennial plants is essential in determining effective methods for weed management in your neck of the woods.
Maintaining A Weed-Free Garden
Maintaining a weed-free yard comes down to a few simple steps, including:
- Monitoring your garden
- Soil testing
- Applying herbicides and mulches

First, to achieve minimal weed growth, regularly monitoring and observing your garden for weed growth is necessary. By catching new weeds from forming early, you can prevent them from spreading throughout your garden and creating an infestation nightmare. Then, you can use some of the tool options listed above, whether hand tools or chemical applications, or roll up your sleeves and do a bit of weekly manual weeding to maintain your green space.
Another critical step in maintaining a weed-free garden is periodic soil testing. Testing can help you determine nutrient densities and establish if your soil needs any amendments or adjustments to support vegetable growth while suppressing weeds. 11
Check Lowest Prices On The Best Soil Test Kits
Lastly, reapplying mulch and herbicides as needed can also help repress weed growth and keep your garden healthy. Remember, a little preventative maintenance goes a long way in keeping your garden clear of pesky weeds!
Conclusion
Effective weed management requires a holistic approach considering environmental impact, human health, and beneficial organisms. Although not all weed-suppressing techniques may be natural, they may all be effective when used properly at the correct times. For example, hand and power tools can be used for smaller backyard gardens, while commercial-grade farm implements can be used for more extensive agricultural operations.
Regular monitoring, periodic soil testing, assessing your weed infestation, prioritizing denser areas, and coordinating with your region’s climate and weather are all effective strategies to help tame those unsightly weeds growing in your vegetable garden.
Likewise, correctly identifying weed classifications offers the humble gardener tremendous knowledge throughout the year about what to expect from their weedy foes and, more importantly, how to combat them effectively. Additionally, reapplying mulch and herbicides when needed can further suppress weed growth.
Since we all know that weeds can be a pesky problem in the garden, following these strategies and taking a proactive approach to weed management can minimize the number of weeds sprouting in your garden while enjoying healthier plants and larger yields all season long.
What methods have you successfully used to help keep weeds at bay in your garden? We’d love to read about your triumphant victory! So drop us a comment below and let us know your success story!
SOURCES
- Wikipedia – Weed
- University Of Georgia, Extension – Weed Control Options For The Home Vegetable Gardener
- Wiley.com – Ecology Of Weeds And Invasive Plants: Relationship To Agriculture And Natural Resource Management, 3rd Edition
- Wikipedia – Herbicide
- The National Gardening Association – Weed Control
- University Of Minnesota, Extension – Using The Sun To Kill Weeds And Prepare Garden Plots
- Almanac – 12 Ways To Kill Weeds Naturally
- University Of Connecticut, Extension News – How To Weed Your Garden: How Often, What To Weed, Tips Or Best Management Practices
- Sage Journals – Weeds In Action: Vegetal Political Ecology Of Unwanted Plants
- National Library Of Medicine, National Center For Biotechnology Information – Herbicides As Weed Control Agents: State Of The Art: I. Weed Control Research And Safener Technology: The Path To Modern Agriculture
- University Of Minnesota, Extension – Flea Beetles







